Let’s take an in-depth analysis of the 58.2 kWh battery version and compare it with 72.6 kWh battery version.
Following the most recent fast charging analysis of the European Hyundai Ioniq 5 with a 72.6 kWh battery, it’s time for an in-depth analysis of the entry-level 58.2 kWh battery version.
One of the early units was recently tested at an IONITY fast charging station by Andreas Haehnel, which allows us to get an idea of what to expect. The outside temperature was 16°C, according to the video.
The results are very interesting so let’s get into details.
Charging power vs state-of-charge (SOC)
The test from 0% to 90% SOC reveals a mostly flat charging curve, that has Ioniq 5’s specific instant power changes and a temporary dip (this time around 60% SOC).
Peak charging power is about 177 kW. As we can see, the highest output is available from about 7% to 45% SOC, then there is a reduction below 145 kW, which stays until 57%. After the temporary dip, the power charging continues at a similar level of around 140 kW for a while. Then we can see a gradual decrease, up to 50 kW at 86%.
At first, we would like to compare the 58.2 kWh battery version with the 72.6 kWh battery version (previous test at IONITY and Hyundai’s manufacturer demo in South Korea).
Comparison of charging power
As we can see, the smaller battery version has a similar charging curve, just the power level appears to be proportionally lower (roughly 20%) to the lower capacity.
The average 20-80% SOC at 144 kW is about 15-20% below the level noted in tests of the larger pack.
| DC Fast Charging Comparison by InsideEVs | |||
| Model [data source] | Drive / Battery (kWh) | Max Power | Avg Power (20-80%) |
| 2021 Hyundai Ioniq 5 (58.2 kWh) [Andreas Haehnel] | AWD 62 kWh | 177 kW | 144 kW |
| 2021 Hyundai Ioniq 5 (72.6 kWh) [Battery Life] | AWD 77 kWh | 224 kW | 170 kW |
| 2021 Hyundai Ioniq 5 (72.6 kWh) (Hyundai’s demo) [Hyundai] | AWD 77 kWh | 225 kW | 180 kW |
Comparison of State-of-charge (SOC) vs time
Charging times appear to be comparable with the bigger battery version.
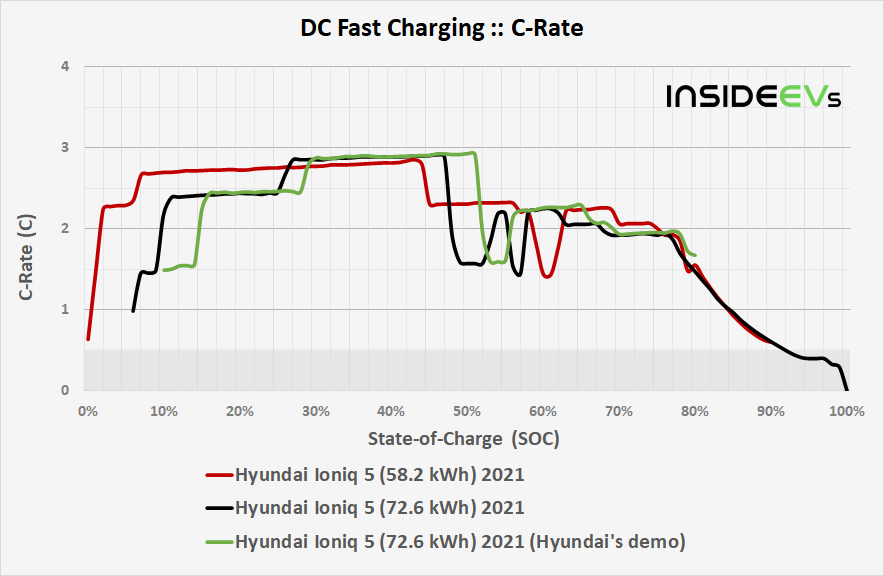
Comparison of C-rate
The main reason behind similar charging time and power level proportional to the capacity is a similar C-rate level for most of the time, under 3.0C peak.
All packs are under a very similar load.
| DC Fast Charging Comparison by InsideEVs | |||||
| Model [data source] | Drive / Battery (kWh) | Max Power | Avg Power (20-80%) | Max C-Rate | Avg C-Rate (20-80%) |
| 2021 Hyundai Ioniq 5 (58.2 kWh) [Andreas Haehnel] | AWD 62 kWh | 177 kW | 144 kW | 2.9 | 2.3 |
| 2021 Hyundai Ioniq 5 (72.6 kWh) [Battery Life] | AWD 77 kWh | 224 kW | 170 kW | 2.9 | 2.2 |
| 2021 Hyundai Ioniq 5 (72.6 kWh) (Hyundai’s demo) [Hyundai] | AWD 77 kWh | 225 kW | 180 kW | 2.9 | 2.3 |
Comparison of range replenishing speed
The main difference between the versions emerges when comparing the range replenishing speed.
The smaller and lighter 58.2 kWh battery version of the car is a few percent more efficient (WLTP), however, it’s not enough to offset the 15-20% difference in charging power. In effect, the bigger battery version replenishes range noticeably faster.
The Hyundai Ioniq 5 (58.2 kWh), despite an outstanding score of 15.2 km/min (9.5 mi/min) is no match for the 72.6 kWh battery version, but it’s one of the top EVs out there and #1 for EVs with a similar battery capacity.
| DC Fast Charging Comparison by InsideEVs | |||
| Model [data source] | Drive / Battery (kWh) | Avg Power (20-80%) | WLTP range rep. rate (20-80%) |
| 2021 Hyundai Ioniq 5 (58.2 kWh) [Andreas Haehnel] | AWD 62 kWh | 144 kW | 15.2 km/min 9.5 mi/min |
| 2021 Hyundai Ioniq 5 (72.6 kWh) [Battery Life] | AWD 77 kWh | 170 kW | 18.8 km/min 11.7 mi/min |
| 2021 Hyundai Ioniq 5 (72.6 kWh) (Hyundai’s demo) [Hyundai] | AWD 77 kWh | 180 kW | 19.9 km/min 12.4 mi/min |
For comparison, Hyundai Ioniq 5 (58.2 kWh) has a higher average than the entry-level Tesla Model 3 (53-55 kWh) or Volkswagen ID.3 (62 kWh): see full report here.
| DC Fast Charging Comparison by InsideEVs | ||||
| Model [data source] | Drive / Battery (kWh) | Max Power | Avg Power (20-80%) | WLTP range rep. rate (20-80%) |
| 2020 Tesla Model 3 SR+ [Fastned] | RWD 53 kWh | 170 kW | 82 kW | 11.4 km/min 7.1 mi/min |
| 2020 Volkswagen ID.3 (62 kWh RWD) [Fastned] | RWD 62 kWh | 100 kW | 70 kW | 8.4 km/min 5.2 mi/min |
| 2021 Tesla Model 3 SR+ [Bjørn Nyland] | RWD 55 kWh | 159 kW | 64 kW | 9.4 km/min 5.8 mi/min |
Conclusions
The conclusion from the DC fast charging test of the Hyundai Ioniq 5 (58.2 kWh) is that it charges great, just like the 72.6 kWh battery version – just proportionally at lower power and lower range replenishing speed. Charging times are basically the same.
There is a strange power dip in the middle of the session, but other than that it’s all ok. There are not many cars that can charge faster at ultra-fast chargers and those that can have bigger packs.
| 2021 Hyundai Ioniq 5 (58.2 kWh) :: DC Fast Charging Summary by InsideEVs Drive: AWD; Battery pack (net / total): 58.2 / 62 kWh [Data source: Andreas Haehnel] | |
| Peak Power Peak C-rate Average Power (20-80% SOC) Time (20-80% SOC) | 177 kW 2.9 144 kW 15 min |
| Range Replenishing Speed (Average 20-80% SOC): | |
| WLTP | 15.2 km/min (9.5 mi/min) |
General info:
* Some values on the charts are estimated from the data source.
** Temperature of the battery cells might highly negatively affect charging capabilities. We don’t have data about temperatures of the battery at the beginning and during the charging process. In cold or hot weather, as well as after driving very dynamically, charging power might be significantly lower than shown on the charts (in extreme cases charging might be impossible until the battery temperature will not return to an acceptable level).
Source: Read Full Article